/
Key Takeaways from the Fortinet Skills Gap Report: Why Cybersecurity Training is Crucial for Mitigating Cyber Risk

Sep 6, 2024
Key Takeaways from the Fortinet Skills Gap Report: Why Cybersecurity Training is Crucial for Mitigating Cyber Risk
The Fortinet 2024 Skills Gap report shines a light on critical issues that plague the cybersecurity industry. Here are our main takeaways.
The recent 2024 Fortinet Cybersecurity Skills Gap Report highlights the growing importance of cybersecurity at the board level, with a focus on holistic approaches to addressing cyber threats. Highlighting a three-pronged approach, the report stresses the importance of cybersecurity training and certifications, building a cyber-aware frontline, and implementing strong security solutions. It reveals that the ongoing skills gap continues to hinder organizations, stressing the importance of targeted cybersecurity training to mitigate risk.
In this post, we’ll cover the report’s key takeaways:
- The lack of skilled and trained security personnel remains a significant liability
- Certifications remain a critical marker of cybersecurity competence
- The complexity and impact of cyber threats is increasing year by year
- The rising financial toll indicates that breaches are becoming more severe
- Boards of directors are increasingly interested in cybersecurity
Boards of directors are taking a more active role in cybersecurity, with 51% of organizations reporting that leaders faced penalties like fines, job loss, or even imprisonment after a cyberattack.
Nearly three-quarters (72%) of boards increased their focus on cybersecurity in 2023, implementing measures such as mandatory cybersecurity training for IT staff (64%), security awareness programs for all employees (61%), and investing in better security solutions (59%). Additionally, 97% of boards now consider cybersecurity a business priority and 56% have discussed increasing IT/security staff.
Penalties are consistent across organizations, regardless of size, with fines being the most common (34%). Organizations must recognize that leadership accountability and proactive measures are essential to mitigating cyber risks effectively.

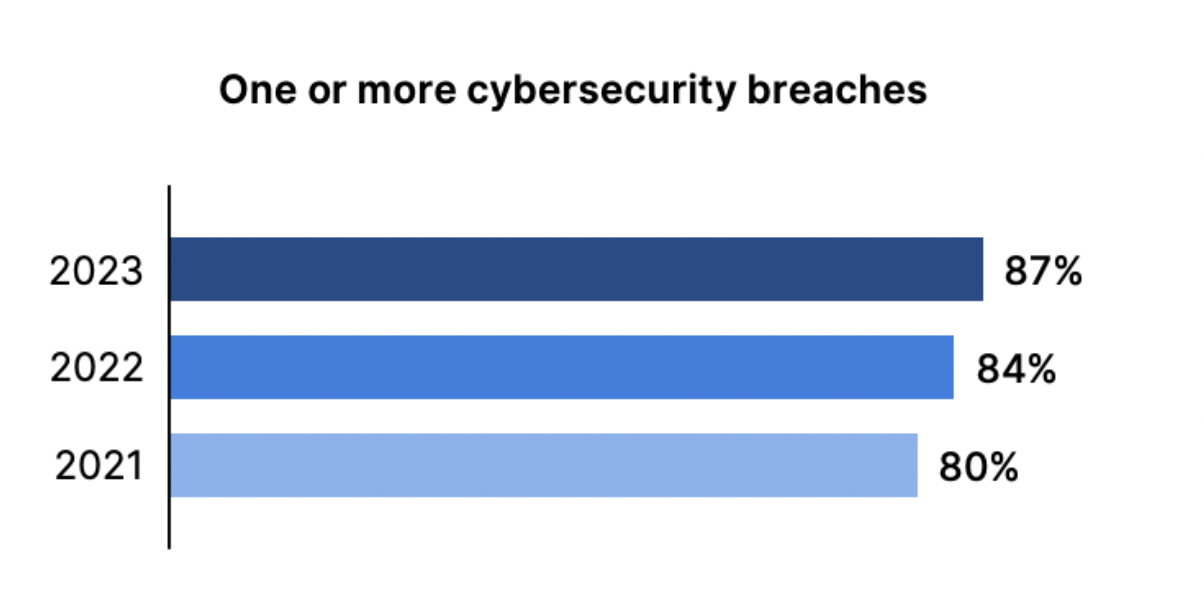
In 2023, 87% of organizations faced one or more security breaches, and over half suffered financial losses exceeding $1 million, a troubling increase from previous years.
This rising financial toll indicates that breaches are becoming more severe, with only 17% of organizations reporting no monetary impact, down from 36% in 2021. The fact that 80% of breaches stem from user-targeted attacks like social engineering and phishing, and malware highlights the critical need for stronger security awareness training. Organizations must address both technical defenses and human vulnerabilities to mitigate these escalating risks.
In 2023, the top five cyberattacks—malware, phishing, web, password, and trojan horse attacks—remained consistent with the previous year, showing the persistence of common threat vectors. Worryingly, recovery times have stretched, with 63% of organizations taking over a month to recover, and 28% needing four months or more. This reflects the increasing complexity and impact of attacks. The fact that 80% of respondents expect cyberattacks to rise, with an anticipated 19.3% increase over the next year, signals a growing sense of urgency for more effective prevention and recovery strategies. Organizations should prepare for prolonged recovery periods and invest in more resilient cybersecurity defenses.

A lack of cybersecurity skills and training remains a significant liability, with 58% of respondents identifying untrained IT staff as a major cause of breaches. Similarly, 56% cite a lack of security awareness, and 54% point to insufficient cybersecurity products. To address these gaps, 65% of organizations plan to expand IT teams, while 62% will mandate cybersecurity certifications, and 61% will implement broader security awareness training. Despite slight improvements, talent recruitment remains a challenge, with 54% struggling to hire skilled professionals, particularly in defensive cybersecurity and cloud security. Retention is improving, but 50% still struggle due to a lack of training and upskilling opportunities.

These statistics highlight the need for ongoing investment in employee education, security solutions, and recruitment strategies to combat cyber risks effectively. The growing skills gap remains a top concern, pushing organizations to address training deficits while improving recruitment pipelines.
Certifications remain a critical marker of cybersecurity competence, with 91% of IT leaders preferring certified candidates. This demonstrates a growing trend, up from 81% in 2021, as certifications validate cybersecurity skills and technical knowledge. While 72% of organizations still find it challenging to recruit certified professionals, this number is improving. The willingness to pay for certifications remains high at 89%, showing organizations’ commitment to upskilling. Certifications directly correlate with enhanced skills, with 61% believing they help keep up with evolving threats. For companies facing frequent attacks, certifications are an essential line of defense.
This data shows a clear trend: certified staff are considered vital to mitigating security risks and are increasingly prioritized in hiring and professional development. While the challenge of recruiting certified talent persists, organizations understand that certification is not just a credential but a key tool in maintaining robust cybersecurity defenses. The willingness to invest in these certifications suggests a long-term strategy to address evolving threats.
As the cybersecurity skills gap widens and cyberattacks become more frequent and costly, organizations are increasingly focused on building a stronger, certified workforce to combat these threats. The statistics reveal a persistent struggle to recruit and retain skilled professionals, coupled with the growing importance of certifications and training.
OffSec plays a crucial role in closing the cybersecurity skills gap by providing training that covers the most in-demand skills, such as cloud security, penetration testing, and security operations. OffSec’s industry-recognized infosec courses and certifications are highly valued by leaders, who overwhelmingly prefer candidates with credentials that validate their expertise.
Given the reported difficulties in recruiting certified professionals, OffSec helps organizations upskill their workforce, filling these talent gaps. Additionally, OffSec’s rigorous training prepares professionals to respond to evolving threats, addressing the need for improved recovery times and resilience highlighted in recent statistics. Our focus on certifications also supports organizations that face challenges in hiring and retaining talent, by fostering employee development and reducing turnover.
By offering practical, hands-on learning that aligns with current security needs, OffSec helps address the key challenges reported by IT leaders—building a more skilled, certified, and resilient cybersecurity workforce to mitigate the increasing threat landscape.

Sara Jelen
Sara Jelen is the Content Marketing Manager at OffSec. Through her extensive work as a writer and content marketer, Sara is specialized in the cybersecurity domain. With a background in anthropology and arts, Sara incorporates a human-centric perspective in exploring cybersecurity topics and the movers and shakers behind it.
Stay in the know: Become an OffSec Insider
Get the latest updates about resources, events & promotions from OffSec!
